As the primary power source for new energy electric vehicles, batteries significantly impact the use of these vehicles. However, the battery's energy is not limitless, requiring replenishment after consumption. The charging system plays a crucial role as the key energy supply system for the operation of electric vehicles, representing an indispensable component in the commercialization and industrialization of electric cars.
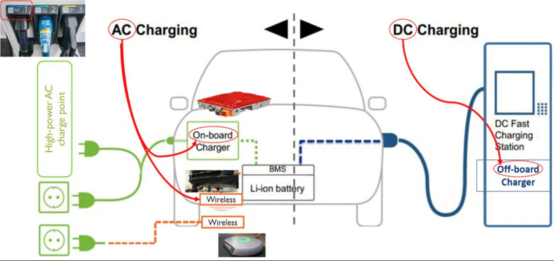
Currently, there are two types of charging stations in the market: Alternating Current (AC) charging stations and Direct Current (DC) charging stations.
Their main differences are as follows:
Firstly, electric vehicles are already equipped with rectifiers. In AC charging stations, the charging process merely outputs a 220V (varies based on different national grid systems) power supply to the charging machine, with the power of the charging station not exceeding the vehicle's motor power. Subsequently, the on-board charging device converts the alternating current from the grid into direct current for battery charging. Constrained by the limited space inside the vehicle, the on-board charging device cannot be too large, and implementing an effective cooling system is challenging. Therefore, charging through AC charging stations is relatively slow and is typically installed in locations like residential parking lots.
In contrast, DC charging stations are different. They come equipped with a rectifier that directly converts the output current into direct current for battery charging. As there are no space limitations, the rectifier's power can be larger, resulting in higher charging efficiency. Consequently, DC charging stations are usually installed at charging stations near highways. Currently, most electric vehicles can charge up to 80% of their battery capacity within 30 minutes when using DC fast charging.
Based on the speed differences between these two charging methods, we further categorize them as fast charging and slow charging, corresponding to DC fast charging and AC charging, respectively.
 Hot News
Hot News